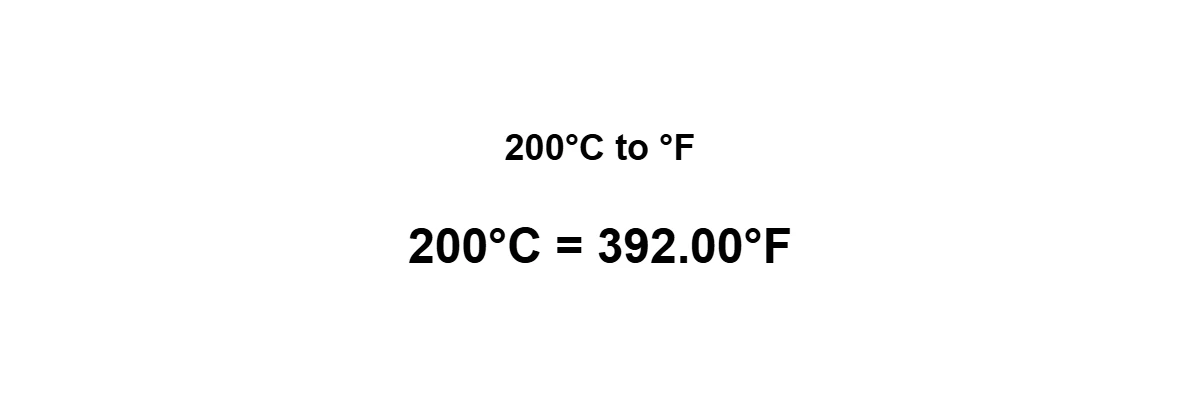
Quick Answer: What is 200°C in Fahrenheit?
200°C = 392°F
Using the formula: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Calculation: (200 × 9/5) + 32 = (200 × 1.8) + 32 = 360 + 32 = 392°F
200 Degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit Conversion
How to Convert 200 Celsius to Fahrenheit: Exact Formula
To convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit, use the following formula:
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Start with the temperature in Celsius: 200°C
- Multiply by 9/5: 200 × 9/5 = 200 × 1.8 = 360
- Add 32: 360 + 32 = 392
- Result: 200°C = 392°F
Celsius to Fahrenheit Converter
Instantly convert °C to °F for free. Ideal for cooking, travel, and science. Get accurate results in seconds!
Need to Convert Another Temperature?
Use our temperature converter to quickly calculate any Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion.
Convert Now200°C in Oven Cooking: Complete Guide
200°C Equivalent in Different Ovens
- Conventional Oven: 200°C = 392°F
- Convection/Fan Oven: 180°C = 356°F (reduce by 20°C)
- Air Fryer: 180°C = 356°F (reduce by 20°C)
- Gas Mark: Gas Mark 6
Cooking Times at 200°C (392°F)
| Food Item | Cooking Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Chicken Breast | 20-25 minutes | Until internal temp 74°C (165°F) |
| Roast Vegetables | 15-20 minutes | Toss with oil for crispiness |
| Cookies | 8-12 minutes | Until edges golden brown |
| Pizza | 12-15 minutes | Crust should be golden |
| Salmon Fillets | 10-12 minutes | Flakes easily with fork |
200°C Comparison with Other Temperature Units
200°C is a common temperature used in cooking and various industrial processes. Here's how it compares to other temperature units like Gas Mark and Kelvin:
- Gas Mark: 200°C is approximately Gas Mark 6. This is a useful reference for those using gas ovens. The conversion from Celsius to Gas Mark helps in adjusting oven settings accurately.
- Kelvin: To convert 200°C to Kelvin, you add 273.15. So, 200°C is 473.15K. Kelvin is often used in scientific and engineering applications.
- 200 F to Celsius: If you want to convert 200°F back to Celsius, you can use the formula: °C = (°F - 32) × 5/9. In this case, 200°F is approximately 93.33°C.
200°C / 392°F Temperature Guide: Applications & Science
At 200°C (392°F), we reach a temperature that's 100 degrees above water's boiling point (100°C/212°F). This high heat creates specific chemical reactions in food and materials:
The Science Behind 200°C Cooking
Maillard reactions accelerate significantly at this temperature, creating complex flavors and golden-brown textures in baked goods and roasted meats. The Maillard reaction – the chemical interaction between amino acids and reducing sugars – reaches optimal levels between 140-200°C (284-392°F).
Convection Oven Adjustments
For convection ovens, you may need to reduce the temperature by 20°C (36°F) or shorten the cooking time by 25% compared to conventional ovens. This is because convection ovens circulate hot air more efficiently, cooking food faster and more evenly. So 200°C in a conventional oven is roughly equivalent to 180°C in a convection oven.
Culinary Applications by Cuisine
- French baking: Used for baguette final baking to create characteristic crispy crust
- Italian cuisine: Traditional pizza baking temperature (wood-fired ovens often reach 400°C+ but home ovens use 200°C as a standard)
- 200°C Oven Recipes: Perfect for roasting vegetables, baking cookies, and cooking casseroles. Try roasting Brussels sprouts at 200°C for 20-25 minutes for crispy edges and tender centers.
- Convection oven tips: When using a convection oven, reduce temperature to 180°C and check food 5-10 minutes earlier than the recipe suggests.
What is 200°C in a fan oven?
For fan ovens, reduce 200°C by 20°C to 180°C (356°F) for equivalent cooking results. Fan ovens circulate heat more efficiently, requiring lower temperatures. See our fan oven temperature conversion chart for detailed adjustments.
How long to cook chicken at 200°C?
Chicken typically takes 20-25 minutes at 200°C, depending on thickness. Always check internal temperature reaches 74°C (165°F) for food safety.
What is 200c in fahrenheit for baking?
200°C equals 392°F, which is a common temperature for baking bread, cookies, and roasting vegetables. It creates a golden-brown crust while cooking the interior thoroughly.
Is 200c hot for an oven?
Yes, 200°C (392°F) is considered a hot oven temperature. It's ideal for roasting meats, baking bread, and creating crispy textures on foods.
Common FAQs: What is 200 Celsius in Fahrenheit?
Q: What is 200c to f?
A: 200 degrees Celsius (200°C) equals 392 degrees Fahrenheit (392°F).
Q: How is 200 Celsius to Fahrenheit calculated?
A: Use the formula °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32. The calculation is: (200 × 9/5) + 32 = 360 + 32 = 392°F.
Q: What is 200 degrees oven temperature?
A: 200°C is equivalent to 392°F, a common temperature for baking bread and roasting meat.
⚠️ 200°C Safety Precautions
- Oven use: Always use dry mitts - 200°C can cause instant burns
- Oil warning: Never add water to hot oil at this temperature (risk of splattering)
- Air fryer: Keep 5cm clearance from walls for ventilation
- Food safety: Use a meat thermometer to ensure poultry reaches 74°C (165°F) internally
Practical Applications of 200°C (392°F)
200°C (392°F) is a high-heat setting used in various cooking applications:
- Baking bread: Many types of bread, like crusty loaves, are baked at 200°C to develop a golden-brown crust.
- Roasting meats: Ideal for searing the outside of meats quickly and then roasting them to perfection.
- Frying: Some deep-frying processes can use this high temperature for a short time to achieve a crispy texture.
- Air frying: Perfect temperature for crispy fries, chicken wings, and roasted vegetables with less oil.
This temperature is important in several industrial processes:
- High-temperature drying: Used to dry certain materials quickly, such as in the paper and textile industries.
- Material processing: Some plastics and composites can be processed at 200°C.
- Heat treatment: In some metalworking processes, 200°C can be part of the heat-treatment cycle.
Around the home, this temperature appears in:
- Oven settings: High-heat setting on most conventional ovens for tasks like broiling.
- Air fryers: Commonly used for frying and roasting foods with less oil.
- Bread machines: Final baking stage for many bread recipes.
- Dehydrators: Some food dehydrators can reach 200°C for quick drying.
Oven Temperature Guide (Fan, Conventional & Fan-Forced)
200°C in Different Oven Types
| Oven Type | Adjusted Temp | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Conventional Oven | 200°C = 392°F | Bread baking, meat roasting |
| Fan Oven (Convection) | 180°C = 356°F (Reduce by 20°C) | Faster, more even baking |
| Fan-Forced (AU/UK) | Same as Fan Oven | Term used in Australia/UK |
| Air Fryer | 180°C = 356°F (Reduce by 20°C) | Crispy foods with less oil |
When to Use 200°C (392°F)?
- Baking - Crusty bread, pizza, pastries
- Roasting - Whole chickens, large cuts of beef
- Broiling - Quick browning of casseroles
- Air frying - Fries, chicken wings, and vegetables
- Toasting - Nuts and seeds for enhanced flavor