Body Temperature & Fever Guide: Adults & Children
What Is a Normal Body Temperature?
Normal body temperature for adults typically ranges from 36.5°C to 37.5°C (97.7°F to 99.5°F). A temperature of 38.0°C (100.4°F) or higher is generally considered a fever.
Your complete Celsius to Fahrenheit reference with fever thresholds, charts, and medical guidance.
Quick Celsius ↔ Fahrenheit Converter
Interactive Temperature Assessment
—
Recommendation:
Analysis for Adult: 37.0°C = 98.6°F
Comprehensive Temperature Reference Chart (Adults & Children)
← Scroll horizontally for full table on mobile →
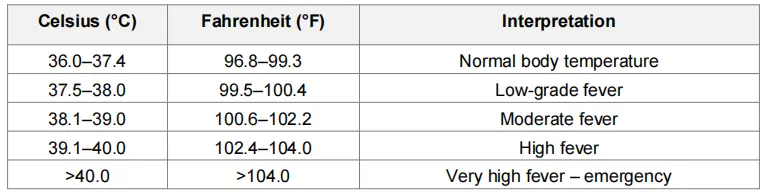
Visual guide to fever temperatures in both Celsius and Fahrenheit
| Status | Celsius (°C) | Fahrenheit (°F) | Adult Advice | Child Advice |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothermia | <36.0°C | <96.8°F | Warm up, monitor | Immediate warming, consult doctor |
| Normal Range | 36.5–37.5°C | 97.7–99.5°F | Healthy | Healthy |
| Slightly Elevated | 37.6–37.9°C | 99.7–100.2°F | Observe, drink fluids | Monitor, reduce activity |
| Low-grade Fever | 38.0–38.9°C | 100.4–102.0°F | Rest, consider medication | Monitor closely, consult doctor |
| Moderate Fever | 39.0–39.9°C | 102.2–103.8°F | Seek medical advice | See doctor immediately |
| High Fever | 40.0–41.0°C | 104.0–105.8°F | Emergency care | Emergency care |
| Dangerous Hyperpyrexia | >41.0°C | >105.8°F | Medical emergency | Medical emergency |
Fever Guides by Age Group
👨⚕️ Adult Fever Guide
- Normal adult body temperature variations
- Typical signs of fever in adults
- Clear indicators for when to seek medical care
- Fever management and medication guidelines
👶 Child & Infant Fever Guide
- Age-based fever thresholds (0–3 months, 3–12 months, 1–12 years)
- Special considerations for children
- Recognizing and managing febrile seizures
- When to call the pediatrician
Fever Temperature FAQs
What temperature is considered a fever?
A body temperature of 38.0°C (100.4°F) or higher is generally considered a fever. Different measurement methods (oral, ear, rectal, forehead) may show slight variations.
What is the normal body temperature in C to F?
The normal body temperature range for healthy adults is typically between 36.1°C (97.0°F) and 37.2°C (99.0°F). This can vary slightly depending on factors such as time of day, activity level, age, and measurement method.
Is 37.5°C (99.5°F) a fever?
This is a borderline temperature, sometimes called a "low-grade" rise. Monitor symptoms and watch for changes. It's not typically considered a true fever but may indicate the beginning of an illness.
When should I see a doctor for fever?
Adults: fever lasting more than 3 days, temperature over 39.4°C (103°F), or accompanied by severe headache, rash, shortness of breath, or stiff neck.
Children: any fever in infants under 3 months, high fever that doesn't respond to medication, or fever with lethargy, irritability, or unusual rash.
How to Measure Body Temperature Accurately
| Method | Normal Range | Best For | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | 36.5–37.5°C | Adults, older children | Avoid within 30 min after eating/drinking |
| Axillary (armpit) | 35.9–36.7°C | All ages | Usually 0.5–1.0°C lower than core temperature |
| Ear (tympanic) | 35.8–38.0°C | 6 months+ | Earwax may affect accuracy |
| Forehead (temporal) | 35.8–37.8°C | Quick screening | May be influenced by environment |
Note on Measurement Differences: Rectal temperatures are generally 0.5°C (0.9°F) higher than oral readings, while armpit (axillary) measurements are usually lower and considered less accurate for core temperature.
Printable Fever Temperature Chart (PDF)
Download our one-page quick reference guide for easy access at home or on your mobile device.
Download PDF ChartImportant Medical Disclaimer
Disclaimer: This guide is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you or your child has a high fever, persistent fever, or symptoms like lethargy, difficulty breathing, or rash, consult a doctor or seek emergency medical care.